 2025-10-17
2025-10-17

What materials are needed to build a metal warehouse?
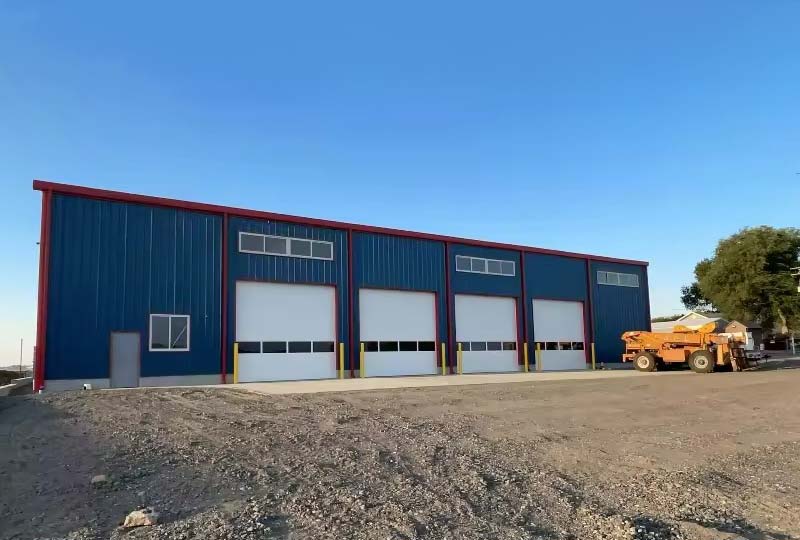
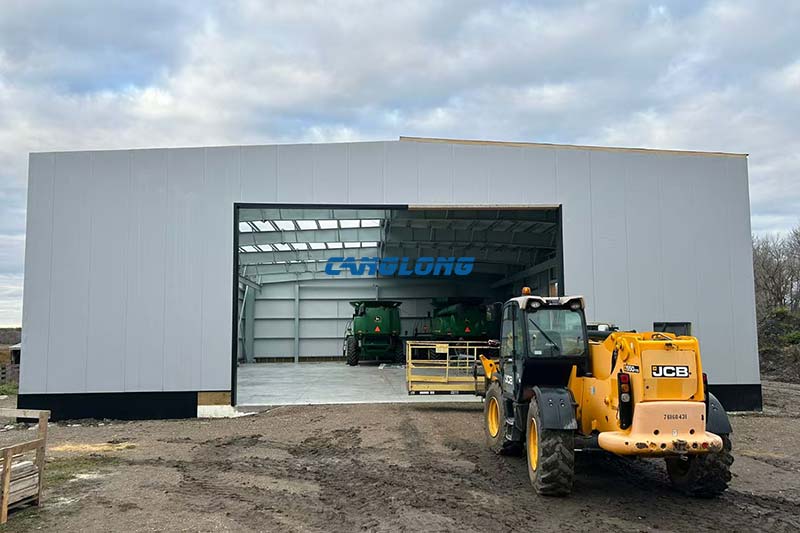
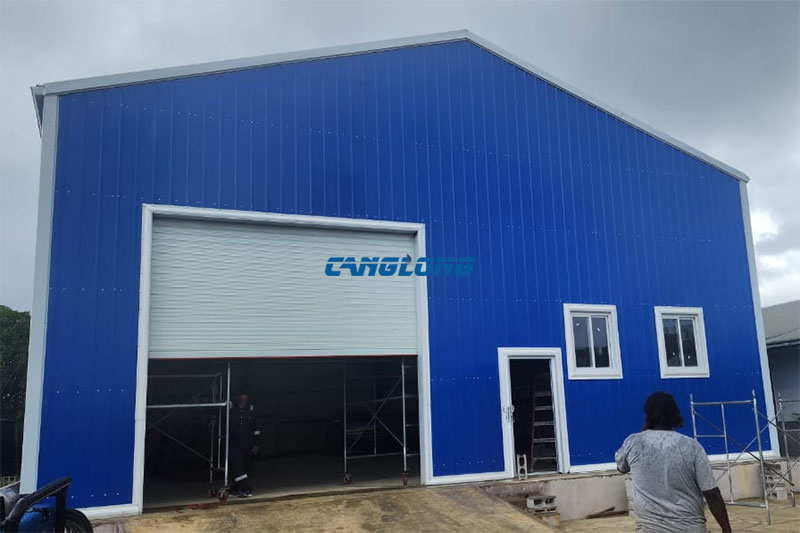
With the surge in industrialization and logistics demand, metal warehouses have become the preferred choice for manufacturers, logistics centers, and e-commerce warehouses due to their high strength, fast construction, low cost, and easy expansion. However, given the differences in climate, load requirements, and regulations across different regions, how should a metal warehouse be built?
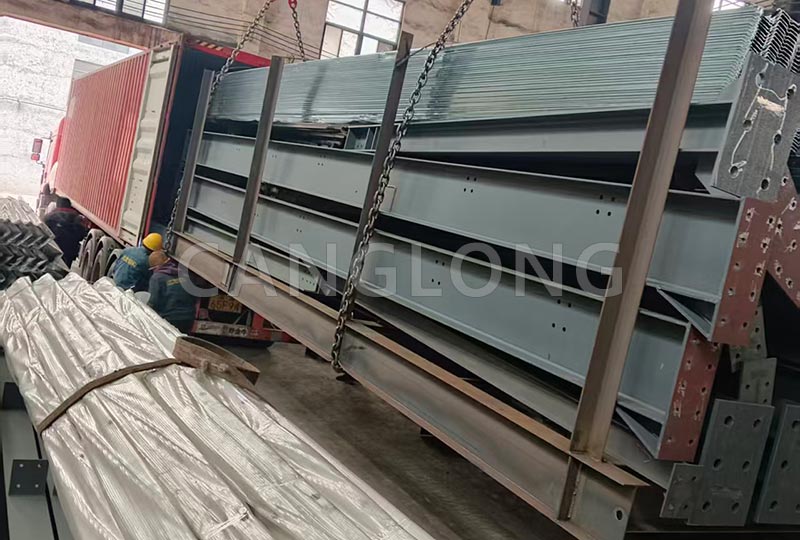
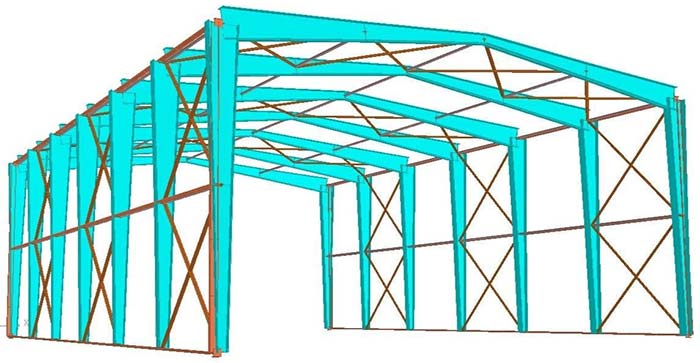
1. Core Structural Materials
The main structure of a metal warehouse is based on steel, whose performance directly impacts the warehouse’s load-bearing capacity, disaster resistance (such as typhoons and earthquakes), and service life. Key materials include:
① Main Load-Bearing Steel
Base Steel Types: Carbon structural steel (such as Q235 and Q345) and low-alloy high-strength steel are the mainstream. Q235 (yield strength 235 MPa) is low-cost and suitable for general warehousing. Q345 (yield strength 345 MPa) offers higher strength and is suitable for large spans (e.g., over 20 meters) or for stacking heavy cargo (such as steel and machinery).
Anti-corrosion Treatment:
- Coastal areas with high salt spray: Hot-dip galvanized steel or double-sided galvanized steel must be used.
- Humid and rainy areas: In addition to galvanizing, an epoxy zinc-rich primer and polyurethane topcoat can be applied for double rust protection.
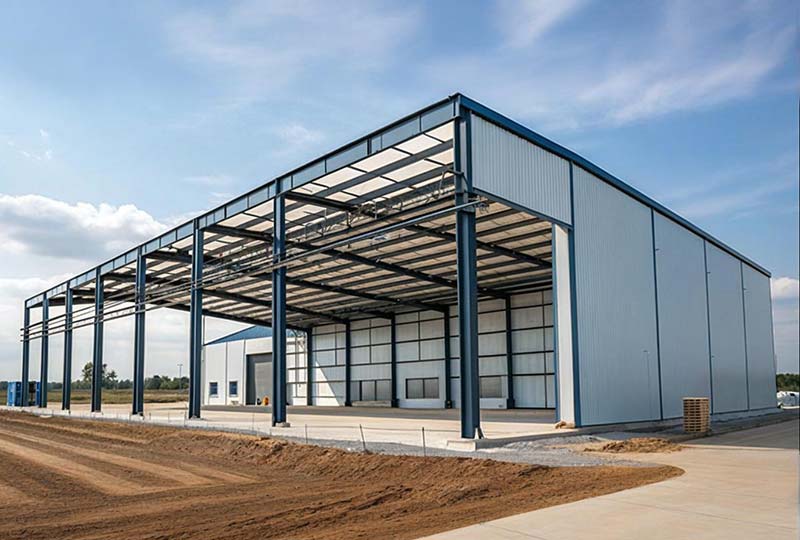
② Structural Frame Components
- Columns: H-shaped steel or square tubes are typically used. The load capacity should be calculated based on the warehouse’s span and height. For example, in areas where containers are stored, the wind load capacity of the columns should be increased by 30%.
- Beams and Purlins: C-shaped steel or Z-shaped steel are commonly used to support the roof panels and walls. Large-span warehouses should use H-shaped steel purlins to prevent deformation.
- Roof Trusses and Trusses: Lightweight warehouses can use cold-formed thin-walled steel trusses, while heavy or large-span warehouses require welded steel trusses.
2. Enclosure System Materials
The exterior enclosure of a metal warehouse not only affects the internal environment but also directly impacts its waterproofing and wind-resistant properties. Targeted selection is required for different climate zones:
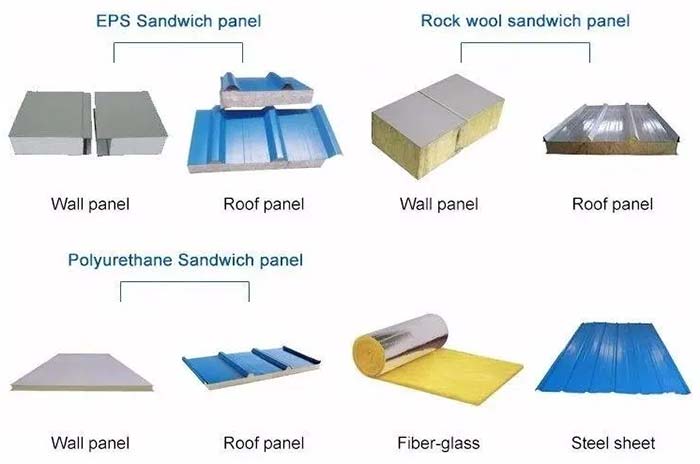
① Roof and Wall Panels
Single-layer color-coated steel panels: Used only for temporary storage or where insulation is not a requirement. Recommended are galvanized color-coated panels with a polyester coating, offering 10-15 years of weather resistance.
Sandwich panels: A more mainstream choice, using the core material to provide thermal insulation, fire resistance, and soundproofing.
- Polyurethane (PU) sandwich panels: With a low thermal conductivity of 0.022 W/m·K, they offer optimal insulation and are suitable for cold regions (such as Northern Europe and Canada) or for storage requiring a constant temperature (e.g., food and pharmaceutical products). However, they are generally rated B2 and require an automatic sprinkler system.
- Rockwool sandwich panels: With a fire rating of A1 and a thermal conductivity of 0.040 W/m·K, they are suitable for hot, dry regions (e.g., the Middle East) or for applications with strict fire safety requirements (e.g., chemical storage).
- Glass wool sandwich panels: Lightweight and sound-absorbing, but relatively low in strength, they are primarily used for small warehouses or auxiliary rooms.
② Accessories
- Panel-to-panel connections: Use concealed snap-lock buckles with EPDM rubber sealing strips to prevent rainwater seepage.
- Ridges and gables: Install aluminum alloy flashings and allow for a 5% slope for drainage to prevent water accumulation and rust.
3. Functional Auxiliary Materials
The value of a metal warehouse extends beyond providing protection from the elements; it must also meet the practical needs of storage, logistics, and personnel operations. The following auxiliary materials are often overlooked but crucial:
① Flooring
Foundation Treatment: Whether constructing a new building or renovating an existing one, a concrete sub-base must be constructed to ensure load-bearing performance.
Surface Options:
- General Use: Diamond abrasive wear-resistant flooring offers low cost and an abrasion resistance of 300-500g/m2, suitable for frequent forklift traffic.
- High Cleanliness Requirements: Epoxy self-leveling flooring, dust-proof and chemical-resistant, 2-3mm thick.
- Cold Chain Warehousing: Non-slip epoxy flooring with a coefficient of friction ≥ 0.6 to prevent ice buildup and slips.

② Functional System Materials
- Ventilation: Roof ventilators or axial flow fans are required in high-temperature and high-humidity areas. Enclosed warehouses can be equipped with fresh air ducts to maintain internal air circulation.
- Fire Protection: Sprinkler systems and smoke detectors are mandatory in most regions of the world. High-risk warehouses require additional gas fire extinguishing equipment.
- Lighting: LED high bay lights with a brightness of ≥ 300 lux or 500 lux are recommended. Explosion-proof LED lights are required in explosion-proof areas.
4. Material Selection Strategies for Different Regions
Metal warehouse materials should adapt to local customs. The following are recommendations for typical regions:
- China/Southeast Asia: High temperatures, high humidity, and frequent typhoons require increased corrosion protection with hot-dip galvanizing and sandwich panels. Roof slopes should be ≥ 10%, and columns should be designed to withstand wind loads by 20%.
- Europe/North America: Focusing on environmental protection and energy conservation, rock wool sandwich panels and double-layer color-coated steel plates are recommended, with epoxy flooring preferred.
- Middle East/Africa: Large temperature swings between day and night and high levels of dust and sand are common. Choose thick galvanized color-coated steel plates to prevent sand erosion. Install dustproof sealant strips on the roof, and ensure dust filtering in the ventilation system.

Conclusion
When constructing a metal warehouse, material selection is essentially a balance between demand, cost, and environmental considerations. Select structural steel based on the weight of the stored goods and the warehouse’s span. Select enclosure materials based on the climate. Add auxiliary systems based on functional requirements. Simply clarify your needs to quickly find the optimal solution. After all, a metal warehouse that lasts for 10 years starts with choosing the right first steel plate.
As a well-known steel structure construction supplier in China, Canglong Group has 20 years of industry experience and provides one-stop steel structure solutions from design to installation. We have a factory of 100000 square meters, and all our products have been certified by ISO and CE, and are sold to over 80 countries and regions worldwide.
Related Posts

 August 6, 2025
August 6, 2025

 August 9, 2025
August 9, 2025

 January 30, 2026
January 30, 2026

 August 13, 2025
August 13, 2025
Leave a Message
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *













